Welcome to the third edition in EDC’s Changing Business Landscape Series, which will be published bi-monthly in the San Diego Business Journal and here on our blog. If you missed them, check out the March and May editions.
Surveying the changing business landscape in San Diego
The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted every facet of life, including how businesses operate. Companies in every industry are rapidly re-evaluating how they do business, changing the way they interact with customers, manage supply chains, and where their employees are physically located. This has massive immediate and long-term implications for San Diego’s workforce and job composition, as well as regional land use decisions and infrastructure investment.
To identify evolving trends in local business needs and operations, ensuring their ability to grow and thrive in the region, EDC is surveying more than 200 companies in the region’s key industries on a rolling basis throughout 2021 to monitor and report shifts in their priorities and strategies. In addition, EDC constructed the San Diego Business Recovery Index (BRI)—a sentiment index to measure companies’ perceptions of current conditions, as well as expectations for the future across several factors such as business development, employment and commercial real estate needs. (An index value >50 reflects expansion, and a value <50 reflects contraction. More information on the index and how it is calculated is available here.)
These insights will help inform long-term economic development priorities around talent recruitment and retention, quality job creation, and infrastructure development. Companies are surveyed on several topics, with varying emphases in each wave.
Here are three key findings from the third wave of surveying conducted in June 2021:
- We are amid a great talent reshuffling. Businesses report increasing difficulty hiring and retaining talent, meanwhile the quits rate is at historic highs.
- Supply chains remain knotted up. The strategic importance of our cross-border trade has never been clearer.
- Space needs are in flux as companies prepare for return to office. Demand for office space may be waning, but life sciences companies are looking to add lab space.
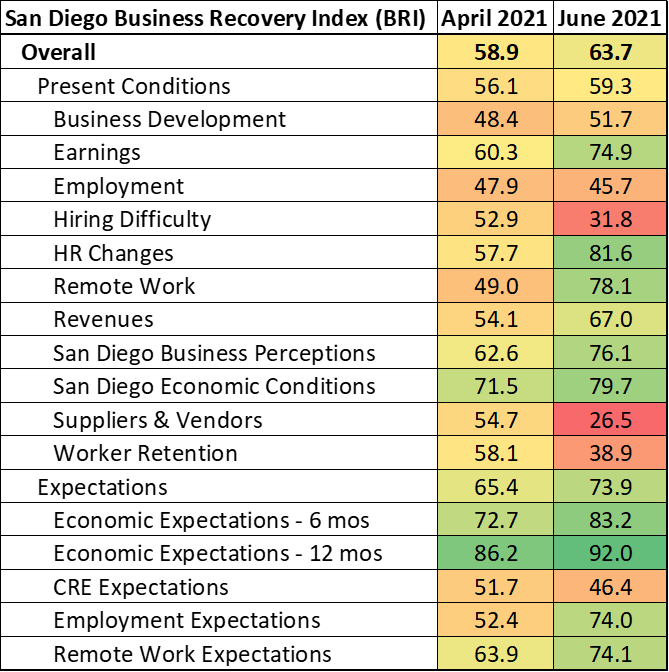
San Diego County firms built on the enthusiasm expressed in April’s survey, with the BRI advancing from 58.9 in April to 63.7 in June. The topline index was pulled higher by more upbeat views of, both, present conditions and expectations for the future. The present conditions index segment rose from 56.1 in April to 59.3 in June while the expectations segment climbed from 65.4 to 73.9 during that time. Business respondents in the region confirmed several trends that have made headlines recently. Companies stated that business conditions have improved significantly over the past two months (due in no small part to California’s reopening in June) while also noting that sourcing talent and suppliers has become significantly more difficult.
A great talent reshuffling
Companies reported that revenues and earnings have improved since April and thus optimism over the next six to 12 months has increased. Expectations are also strong in San Diego’s Innovation cluster. Businesses in this group conveyed that they plan to hire more aggressively in the coming months. This is particularly good news, since each new Innovation job supports another two jobs elsewhere in the regional economy.
Nonetheless, companies also reported having a tougher time attracting new talent as well as increased difficulty retaining existing workers. There has been much ado about labor shortages and the impact of increased and extended unemployment benefits, but the data show that there is a much more nuanced story. First, there is a large mismatch between the talent in-demand and the talent available to work. As of May (most recently available data at time of writing), there were 104,400 people unemployed in the San Diego region and more than 115,000 job openings. However, the top hiring industries are Administrative and Support Services, Professional Services and Manufacturing industries (nearly 40 percent of unique postings), whereas the bulk of the unemployed come from Leisure and Hospitality.
Second, there are record numbers of workers quitting their jobs. The Bureau of Labor Statistics measures the proportion of workers who voluntarily leave their job relative to total employment. This “quit rate” sat at 2.5 percent in May 2021 after falling from 2.8 percent in April—the highest ever recorded. The Conference Board survey’s labor market differential, another measure of views on whether jobs are plentiful or hard to get, vaulted from 36.9 in May 2021 to 43.5 in June. That is the highest level since 2000.
All this quitting not only reflects confidence in the availability of work, but also the changing needs and desires of workers. The San Diego Association of Governments surveyed both employers and employees earlier this year and found that only 36 percent of employers expect to have one or more employees working from home at least one day per week. Meanwhile 44 percent of employees surveyed expect to work from home an average of 1.2 days per week. This difference in expectations partly reflects differences in opinion of how remote work has impacted productivity—only nine percent of employers reported increased productivity during the pandemic versus 48 percent of employees.
Flexibility will be key to keeping and attracting the best and brightest of workers. Perhaps the companies EDC surveyed understand this better than most, as they indicated both improved efficiencies from, as well as increased planned future utilization of, remote work technologies in June compared to April.
Investing in supply chains locally, binationally
Hiring challenges are also impacting supply chains globally. Companies reported a sharp decrease in the accessibility and reliability of their suppliers and vendors. Here, BRI fell from 54.7 in April to a categorical low of 26.5 in June. This corroborates the headlines regarding shortages in lumber and microchips, which has in turn stalled production of higher end goods and led to spikes in commodity prices and other item such as used cars. A lot of these supply chain disruptions are temporary in nature, directly linked to safety measures and restrictions associated with pandemic (this is why longer-term inflation expectations remain stable).
Ports and businesses across the country have experienced ongoing shortages of labor, containers, truck chassis, and more; shipping vessels have been forced to wait in harbors, in some cases for more than two weeks. This global traffic jam has impacted schedule reliability so profoundly it has forced companies to revisit the ways in which they manage risk. Many companies have moved from a just-in-time strategy to just-in-case. This means firms now keep additional inventory on hand, anything from raw materials to the final product. The lack of supply and rising costs have disproportionately impacted small and mid-market suppliers and buyers. This has resulted in direct capital investment from smaller buyers into smaller suppliers to stabilize supply chains and build necessary redundancies.
The pandemic-induced constraint on the movement of goods has only exacerbated trends from the past few years. Trade wars, changing consumer behavior, and e-commerce were already disrupting global supply chains, all of which has highlighted the strategic importance of supply chain management as well as the region’s bi-national assets. The Cali Baja Binational Mega Region is already vertically integrated in Manufacturing, and a warehousing boom in Otay Mesa is increasing capacity for goods coming via land and sea. Cali Baja is an ideal location for companies that want to move operations closer to home but maintain a binational advantage. Continued investment in trade infrastructure, such as our ports of entry and direct route service, will further cement Cali Baja as a binational innovation hub.
The return to office will be in a lab
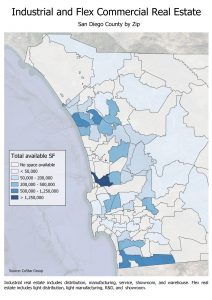
Back in April, companies indicated a modest desire to increase their physical footprint upon returning to the office. However, companies appear to be less sure as the return approaches. In June, companies expressed plans for a net reduction of space, but a deeper dive into the responses reveals that it is demand for office space that is waning. In fact, there is increasing demand for commercial space—life sciences companies in need of laboratory space. This reflects the influx of investment and rapid hiring we are seeing in these industries, as they lead the fight against the global pandemic. Fortunately, there is nearly 10 million square feet of industrial and flex space across San Diego County currently available for lease or purchase that could potentially accommodate this demand. Current hot spots include Sorrento Valley, Vista, and Otay Mesa; Downtown San Diego is also building capacity rapidly.
The headline story is a positive one for San Diego’s economy, but sentiment is far from identical across business sizes and industries. For example, small companies with fewer than 50 workers logged BRI of 53, which is modestly in expansionary territory, while companies with 250 or more employees measured an index value of 63.7. This makes sense, because San Diego’s Leisure and Hospitality businesses tend to be smaller establishments and were the hardest hit during the pandemic. While companies are enthusiastic to get back to full capacity and add workers, it will likely take a few more months for supply chains and the labor market to normalize again. The pandemic is a generational disruption with widespread ramifications, accelerating several trends already underway, including how and where people are willing to work.
Stay tuned for more on San Diego’s changing business landscape. EDC will be back every other month with more trends and insights. For more data and analysis visit: sandiegobusiness.org/research.
This research is made possible by:
