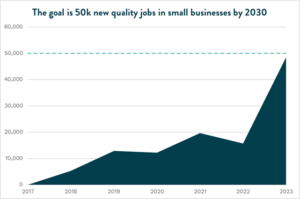
To celebrate and inspire the efforts of regional employers, EDC’s Inclusive Growth blog series highlights San Diego companies and organizations helping to drive progress on the 2030 Inclusive Growth goals. Below we feature San Diego’s comprehensive human services provider Neighborhood House Association (NHA).
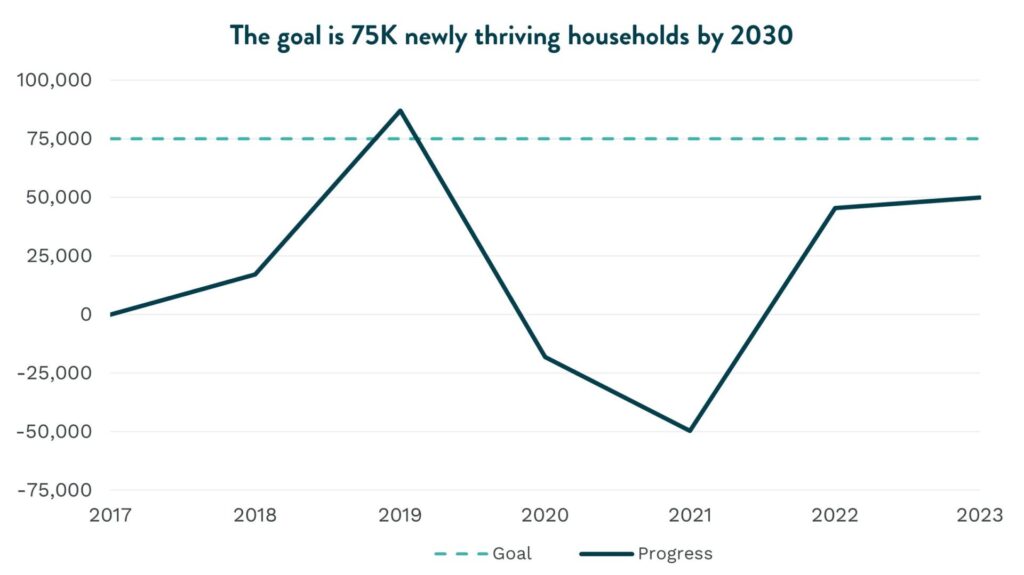
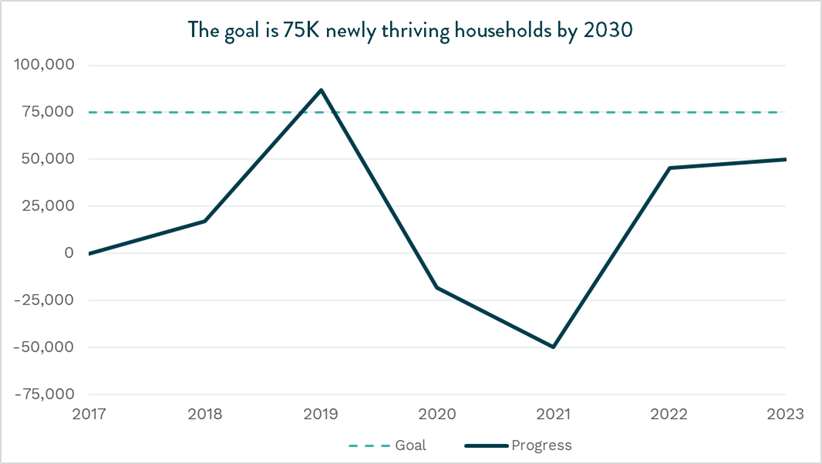
Launched in 2018 and informed by a partnership with the Brookings Institution, the Inclusive Growth initiative sets 2030 goals including increasing the number of thriving households locally, and making the business case for economic inclusion. Decreasing affordability in San Diego threatens progress toward all of the goals and disproportionately impacts communities of color. Household incomes have not kept pace with the cost-of-living, leaving only one in 10 households able to afford the median-priced home in the region. As of 2023, San Diego has added 49,916 newly thriving households (chart below) bringing the total number of San Diego’s thriving households in the region to 610,983.
Supporting households through a continuum of education and wellness
The Neighborhood House Association (NHA) was founded during the settlement house movement in 1914 to assist immigrants as they transitioned to living in the country.
NHA today
As a major employer and one of the largest nonprofit social services agencies in San Diego, NHA works through its Continuum of Care Model, a wrap-around service delivery model supporting households from prenatal to senior care. Its mission: To enrich lives through a continuum of education and wellness services, nurturing children and families from the earliest stages of life through adulthood, providing youth development and career exploration opportunities that allow them eventually to join the region’s workforce with a direct pipeline to workforce opportunities within NHA.
Challenges in grant-funded household support
Currently, NHA supports more than 5,000 community members by advocating for additional funding that addresses household affordability and accessibility challenges to realize dreams for as many households as possible. Because healthy and educated communities are where dreams become reality.

With federal and state grants, each program participant is assisted through a two-year enrollment period with direct support from an NHA family service worker outlining goals and needs, often including early childhood education programs and childcare services. Funds allow for more classrooms slots for children meaning that parents in households and members of the NHA workforce can go to work and school. With this, NHA sustains competitive pay with cost-of-living adjustments alongside annual merit increases to attract the best teaching and support staff for households.
 Most of NHA’s programs are funded by federal and state grants, and as funding for programs like Head Start is challenged at the federal level, NHA continues to actively work with regional, state, and national leaders to ensure that program participants and employees are self-sufficient in supporting themselves and their families.
Most of NHA’s programs are funded by federal and state grants, and as funding for programs like Head Start is challenged at the federal level, NHA continues to actively work with regional, state, and national leaders to ensure that program participants and employees are self-sufficient in supporting themselves and their families.
In addition to visiting state and national offices, NHA invites lawmakers to visit NHA to see programs at work in-person with the goal of increasing visibility and understanding of how the agency impacts the local economy. With an economic impact of more than $200 million each year, NHA operations are making a difference in the lives of team members, program participants, and the entire San Diego region.
As a large local nonprofit, NHA often highlights its value in San Diego’s economic development as a major local employer that allows pathways to education and workforce development. NHA President and CEO Rudy Johnson and have both served on the EDC Board of Directors and strongly believe in EDC’s work. NHA has found great value in joining EDC’s leadership trips and is a proud endorser of the Inclusive Growth initiative.
Join the movement
Progress on EDC’s 2030 Inclusive Growth goals is only achievable with and through the region’s employers scaling innovative and intentional solutions. Organizations like NHA are helping to collectively pave the way toward a more inclusive regional economy.
- Endorse the goals, and be part of the change San Diego’s economy demands.
- Dive into our Inclusive Growth Spotlight Series, including SBCS, Cultura, General Atomics, and more.
To learn more and get involved in EDC’s work, contact:

Bree Burris
Sr. Director, Communications & Community Engagement