Welcome to the second edition in EDC’s Changing Business Landscape Series, which will be published bi-monthly in the San Diego Business Journal and here on our blog. If you missed the first edition, read it here.
Surveying the changing business landscape in San Diego
The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted every facet of life, including how businesses operate. Companies in every industry are rapidly re-evaluating how they do business, changing the way they interact with customers, manage supply chains and where their employees are physically located. This has massive immediate and long-term implications for San Diego’s workforce and job composition, as well as regional land use decisions and infrastructure investment.
To identify evolving trends in local business needs and operations, ensuring their ability to grow and thrive in the region, EDC is surveying more than 200 companies in the region’s key industries on a rolling basis throughout 2021 to monitor and report shifts in their priorities and strategies. In addition, EDC constructed the San Diego Business Recovery Index (BRI)—a sentiment index to measure companies’ perceptions of current conditions, as well as expectations for the future across several factors such as business development, employment and commercial real estate needs. Review the BRI concept and methodology here.
These insights will help inform long-term economic development priorities around talent recruitment and retention, quality job creation and infrastructure development. Companies are surveyed on several topics, with varying emphases in each wave.
Here are three key findings from the second wave of surveying conducted in April 2021:
- The worst of the pandemic is behind us. Companies are very bullish about the next six to 12 months and, as a result, plan to accelerate hiring.
- San Diego’s innovation cluster is (mostly) booming. Life Sciences companies lead the way while Cyber and Aerospace firms are still working through pandemic-related challenges.
- Companies are seriously reevaluating their space needs. Smaller firms are looking to expand their footprint, while traditional Tech companies may be scaling down.
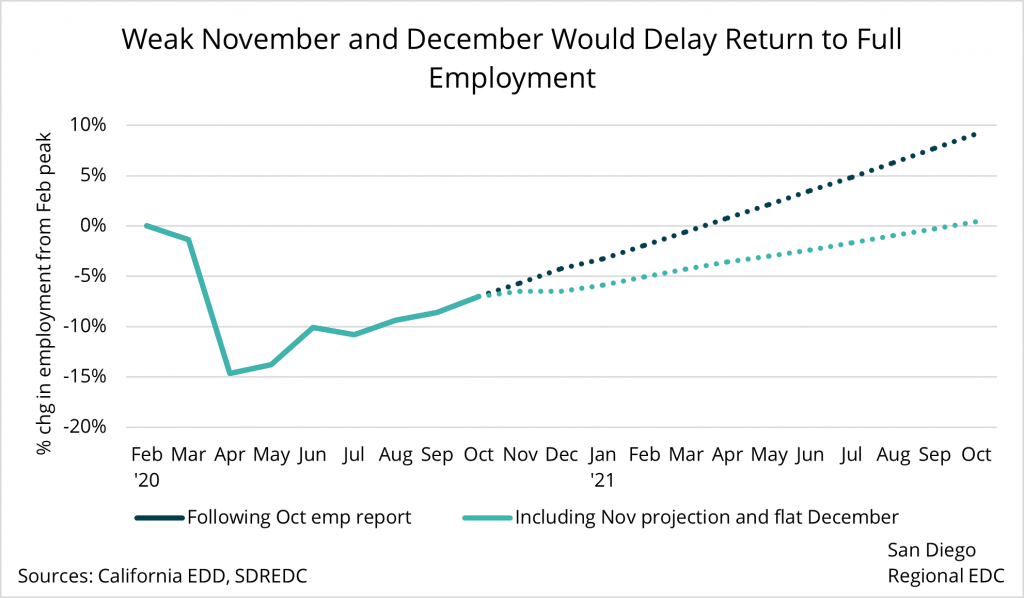
The worst is behind us
San Diego companies indicated that they think the worst of the pandemic has passed. With a BRI of 58.9 in April, regional firms noted that they plan to hire or rehire workers at a slightly faster pace than they have up to this point, while also expanding remote work capabilities going forward.
Last month’s index reading reflects bullish assessments of, both, present conditions (the present conditions subindex registered a value of 56.1) and expectations for the future (subindex of 65.4). Companies noted some lingering effects from a full year in lockdown, including difficulties with business development and job losses, and neutral to slightly negative feelings on remote work over the past year. Nonetheless, firms reported bright views on the current state of the regional economy and noted that San Diego businesses and key industries have adapted to the pandemic better that those in peer regions.
Regional companies were even more upbeat when it came to expectations for the future. All of the index’s expectations subindex values were north of 50, and companies overwhelmingly believe that the regional economy will have improved significantly in the next six months (subindex of 72.7) and even more so within the next 12 months (subindex of 86.2). This is important because many companies make decisions today based on their assessments of business conditions in the near future.
Most companies shared in the optimism, but to varying degrees. Small companies with fewer than 50 employees that were hardest hit during the pandemic held slightly dimmer, though still generally positive, views than their larger counterparts. In particular, smaller firms cited ongoing difficulties accessing new customers, managing suppliers and vendors, and hiring and retaining workers. Even so, assessments of current earnings trends were only slightly negative, and small firms held a sunny disposition when it comes to the current state of the San Diego economy and business climate.
Interestingly, however, companies with fewer than 50 workers had the highest level of optimism for the future across business size cohorts, which could signal an inflection point for the pace of hiring in the coming months. This bodes especially well for the jobs recovery heading into the second half of 2021, as 96 percent of San Diego’s businesses have fewer than 50 employees and small businesses have historically accounted for roughly half of all job growth.
San Diego’s innovation cluster is (mostly) booming
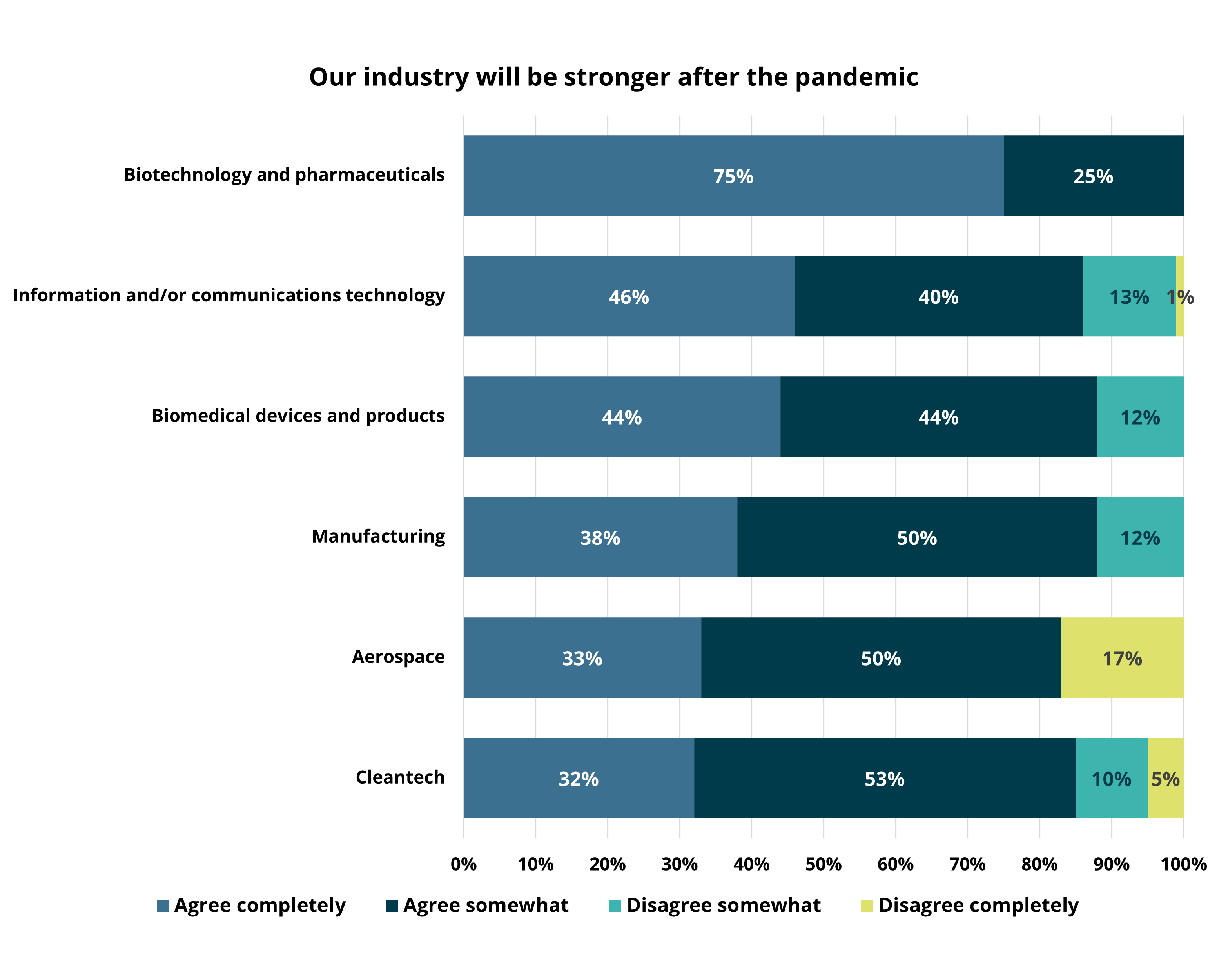
San Diego’s innovation cluster overwhelming expressed optimism entering 2021, as companies shifted toward meeting the demand for life-saving technologies, treatments and personal protective equipment leading to record venture capital investment and renewed job growth. However, a closer look reveals mixed results within the cluster. Industries like Cleantech, Software and Biomedical Device producers all held especially confident views (BRIs in the mid-60s), while Telecommunications, Cybersecurity and Aerospace each signaled ongoing challenges from the pandemic (BRIs ranging from 43 to 50).
Biotech and Biomedical Device manufactures hold strong expectations for the regional economy, with plans to increase their headcount and real estate footprint during the next year. In addition, they expect to increase their use of remote work over the same time frame. While this may seem contradictory, it reflects the modifications and enhancements that many companies are making to protect workers on the production floor, as well as those necessary to attract workers back into the office. Workers want to feel safe once back on company property and they also want to maintain the flexibility that working remotely has provided. To accommodate these needs, employers are preparing for a flexible or hybrid workplace once reopen. In addition, many companies are reconfiguring and even seeking new space to keep workers spread out, adapting space to be more comfortable in a post-pandemic environment. This includes ‘hoteling’ and ‘neighborhooding’ models to help reduce the flow of people and simultaneously allow teams to collaborate in person. Companies are preparing for a gradual return to the office to give workers adequate time to warm up to pre-pandemic routines. More on that below.
While Telecommunications and Cybersecurity firms all share this optimistic regional economic outlook with their Life Sciences peers, these industries are much more subdued about their own expansion plans for the next year. On net, they see their needs for space as unchanged, with some modest reductions in hiring compared to typical years. This reflects the challenges these industries have faced during the pandemic, namely with respect to increased difficulty with sales, hiring and, somewhat surprisingly, inefficiencies from remote work. Aerospace has not yet recovered from the initial impacts of the pandemic, still reeling from significant hits to both sales and employment, as well as disruptions in their supply chains from lockdowns and restricted international travel and transportation.
Smaller firms are looking to add space
After more than a year of implementing remote work and reduced onsite staffing, companies are beginning to plan for a return to the office. However, how much space awaits those returning to the office will vary by industry as well as firm size.
It is small- and medium-sized firms that are looking to expand their commercial real estate footprint over the next year rather than larger firms. In fact, the proportion of firms surveyed that expect to increase space by 10 percent or more of their current square footage is nearly double that of those planning to reduce their current space by 10 percent or more (16 percent to 8.4 percent, respectively). However, when you factor in the size of each company, those planning significant real estate growth represent only three percent of the jobs compared to 13 percent of jobs for those looking to reduce space significantly (companies surveyed collectively employ nearly 200,000 workers).
When we look at the innovation companies, we see some stark differences between traditional Technology and Biotechnology industries. Eight percent of respondents representing 22 percent of jobs plan to reduce their space by more than 10 percent—mostly in the Telecommunications industry. However, nearly 26 percent of respondents representing 41 percent jobs expect to add modest amounts of space less than 10 percent of their current footprint. Here many respondents are in the Biomedical Device and Biotech industries and likely in need of additional production or lab space.
Understanding these evolving and distinct trends is important because San Diego’s innovation cluster is leading the region out of this pandemic-driven economic downturn, just as it has in each past downturn. Each job added in the innovation cluster supports another two jobs elsewhere in the economy. Yet, these innovation companies do not necessarily need to be physically located in San Diego in order to operate. Making sure these companies have the infrastructure and access to talent that they need to flourish is critical to our region’s prosperity.
Stay tuned for more on San Diego’s changing business landscape. EDC will be back every other month with more trends and insights. For more data and analysis visit: sandiegobusiness.org/research.
This research is made possible by: